Hertzsprung Russell diagram worksheet answers unveil the intricacies of stellar evolution and classification, providing a comprehensive understanding of the celestial tapestry. Embark on an illuminating journey through the cosmos, deciphering the language of the stars.
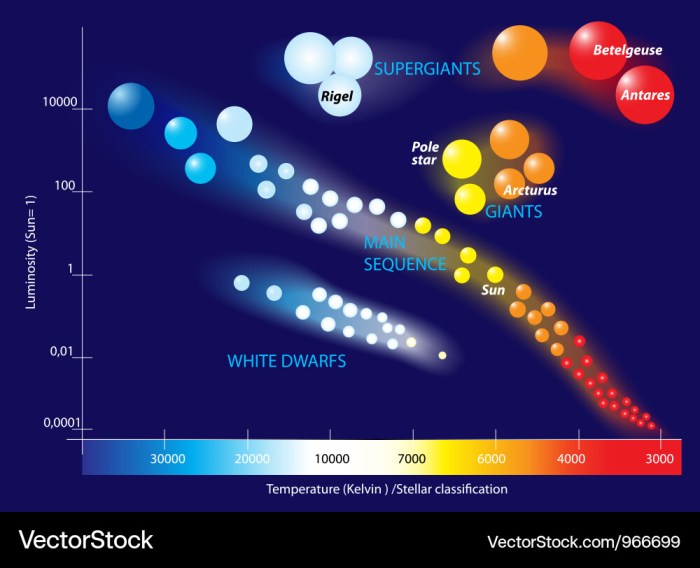
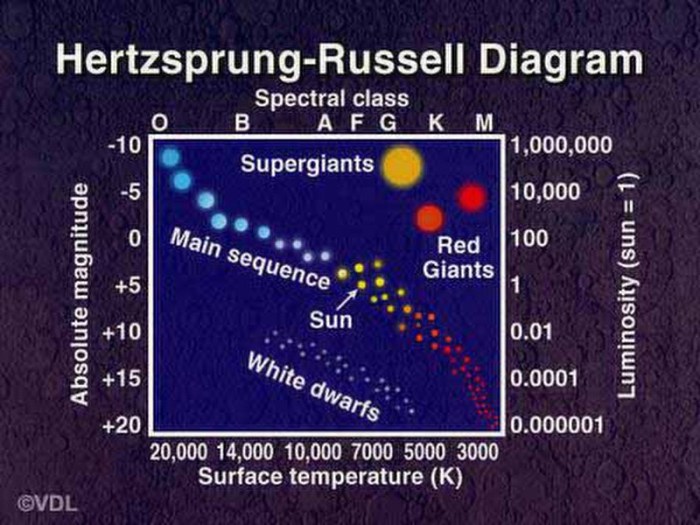
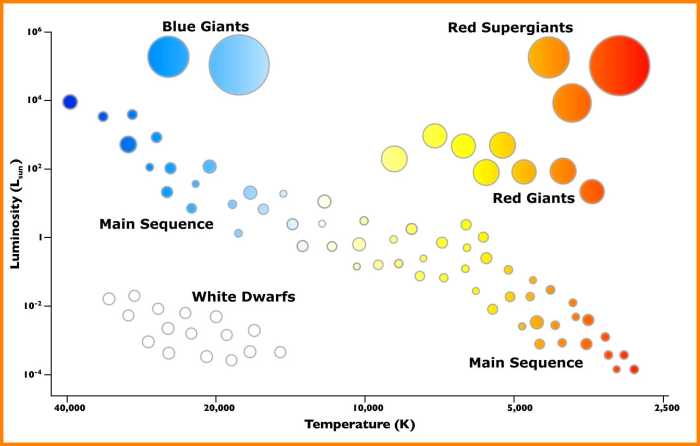
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram serves as a celestial map, charting the diverse characteristics of stars across the universe. Its axes delineate stellar temperature and luminosity, revealing the evolutionary paths of these celestial beacons.
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Overview
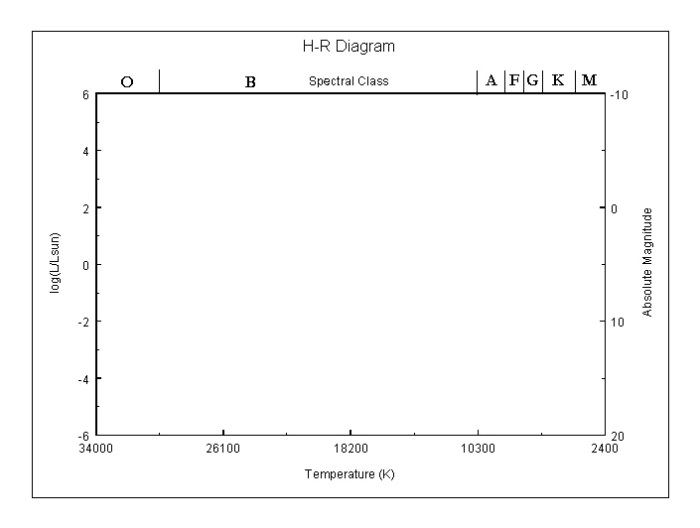
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graphical representation of the relationship between the luminosity and surface temperature of stars. It is a fundamental tool in stellar astrophysics, providing insights into the evolution and properties of stars.
The H-R diagram is constructed by plotting the absolute luminosity of stars (a measure of their total energy output) against their effective surface temperature. The absolute luminosity is typically measured in solar luminosities (L ☉), while the surface temperature is expressed in Kelvin (K).
Stellar Classification on the H-R Diagram
Stars are classified into different spectral classes based on their position on the H-R diagram. The main spectral classes are:
- O stars:Hottest and most luminous stars, with surface temperatures exceeding 30,000 K.
- B stars:Hot and luminous stars, with surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K.
- A stars:Intermediate temperature and luminosity, with surface temperatures between 7,500 and 10,000 K.
- F stars:Slightly cooler and less luminous than A stars, with surface temperatures between 6,000 and 7,500 K.
- G stars:Similar to our Sun, with surface temperatures between 5,200 and 6,000 K.
- K stars:Cooler and less luminous than G stars, with surface temperatures between 3,700 and 5,200 K.
- M stars:Coolest and faintest stars, with surface temperatures below 3,700 K.
Stellar Evolution on the H-R Diagram, Hertzsprung russell diagram worksheet answers
The H-R diagram also provides insights into the evolution of stars over time. As stars burn through their nuclear fuel, they evolve through different stages, which are reflected in their position on the H-R diagram:
- Main sequence:Most stars spend the majority of their lives on the main sequence, where they fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores.
- Red giant:When stars exhaust their hydrogen fuel, they expand and cool, becoming red giants.
- White dwarf:After shedding their outer layers, red giants collapse into dense, compact white dwarfs.
Interpreting H-R Diagrams
H-R diagrams can be used to understand the stellar populations of different environments:
- Open clusters:Contain young stars that are still on the main sequence.
- Globular clusters:Contain older stars that have evolved off the main sequence.
- Galaxies:Show the distribution of stars of different ages and compositions.
H-R Diagram as a Tool for Stellar Astrophysics
The H-R diagram is a powerful tool for studying the properties of stars:
- Stellar masses:The position of stars on the main sequence can be used to estimate their masses.
- Stellar temperatures:The temperature of stars can be inferred from their color and luminosity.
- Stellar luminosities:The luminosity of stars can be determined from their absolute magnitude and distance.
- Stellar distances:The distance to stars can be estimated using their apparent magnitude and luminosity.
FAQ Resource: Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Worksheet Answers
What is the significance of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a comprehensive overview of stellar characteristics, allowing astronomers to classify stars based on their temperature, luminosity, and evolutionary stage.
How does the H-R diagram illustrate stellar evolution?
The H-R diagram depicts the evolutionary tracks of stars, showcasing their movement through different stages of their lifespan, from the main sequence to the red giant and white dwarf phases.
What are the main spectral classes of stars?
The primary spectral classes are O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, each characterized by specific temperature ranges and spectral features.