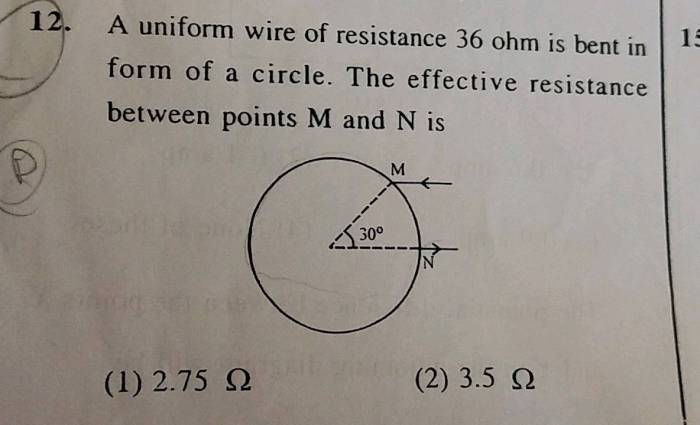
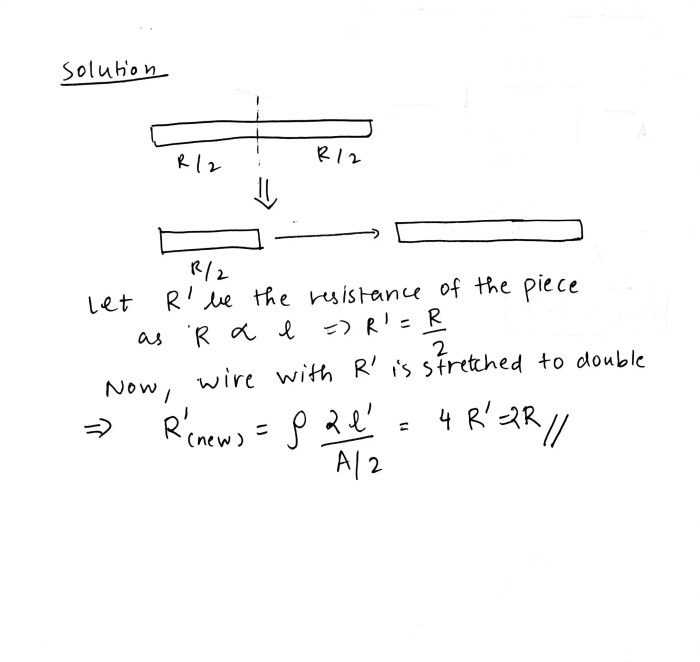
A wire with a resistance of 6.0 ohm is drawn – In the realm of electrical engineering, the concept of resistance plays a pivotal role in shaping the behavior of circuits. This article delves into the intricate details of drawing a wire with a specific resistance of 6.0 ohms, exploring the underlying principles, practical considerations, and diverse applications of this essential component.
Ohm’s Law, the cornerstone of electrical theory, establishes the fundamental relationship between resistance, voltage, and current. By manipulating these parameters, engineers can tailor the electrical properties of wires to meet specific design requirements.
Wire Resistance and Ohm’s Law: A Wire With A Resistance Of 6.0 Ohm Is Drawn

Electrical resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a conductor. Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between resistance (R), voltage (V), and current (I): V = IR.
Resistance depends on the material, length, and cross-sectional area of the conductor. For example, copper has a lower resistance than aluminum.
Drawing a Wire with a Specific Resistance, A wire with a resistance of 6.0 ohm is drawn
To draw a wire with a specific resistance, determine the required length and diameter based on the material’s resistivity and the desired resistance.
The formula for calculating the length (L) of a wire is: L = (R – A) / (ρ – π – r^2), where A is the cross-sectional area, ρ is the resistivity, and r is the radius.
Applications of Wires with Specific Resistance
Wires with specific resistance are used in various applications, including:
- Resistors: To control current flow and voltage
- Heating elements: To generate heat
- Sensors: To measure temperature, pressure, or other parameters
Comparison of Different Wire Materials
| Material | Resistivity (μΩm) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 1.68 | High conductivity, malleability | Expensive |
| Aluminum | 2.65 | Lightweight, low cost | Lower conductivity than copper |
| Silver | 1.59 | Highest conductivity | Very expensive |
Design Considerations for Wires with Specific Resistance
When designing wires with specific resistance, consider:
- Insulation: To prevent short circuits and ensure safety
- Flexibility: For ease of installation and handling
- Durability: To withstand environmental conditions
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of wire resistance in electrical circuits?
Wire resistance plays a crucial role in determining the flow of current and voltage in a circuit. It affects power dissipation, voltage drop, and circuit efficiency.
How is the resistance of a wire calculated?
The resistance of a wire can be calculated using the formula: Resistance = Resistivity – Length / Area, where Resistivity is a material property, Length is the wire’s length, and Area is its cross-sectional area.
What factors influence the resistance of a wire?
The resistance of a wire is primarily influenced by its material, length, diameter, and temperature.