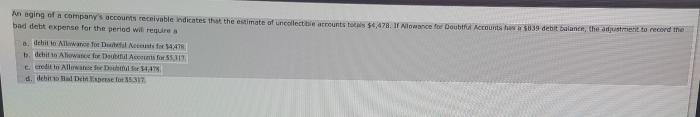
An aging of a company’s accounts receivable indicates that the business is facing challenges in collecting payments from its customers. This can have a significant impact on a company’s cash flow and profitability, and it can also be a sign of underlying financial problems.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to an aging accounts receivable, including slow-paying customers, inefficient billing practices, and economic downturns. Whatever the cause, it is important for businesses to take steps to address the issue, as it can have a negative impact on their financial health.
Accounts Receivable Aging: Definition and Importance
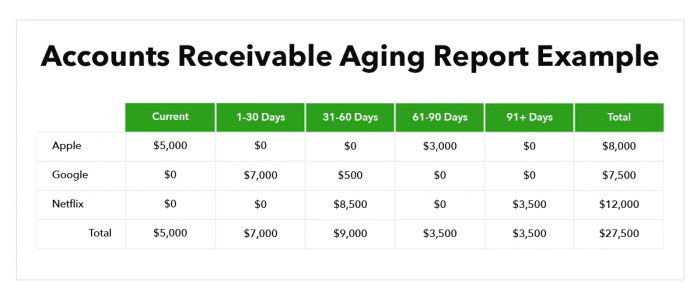
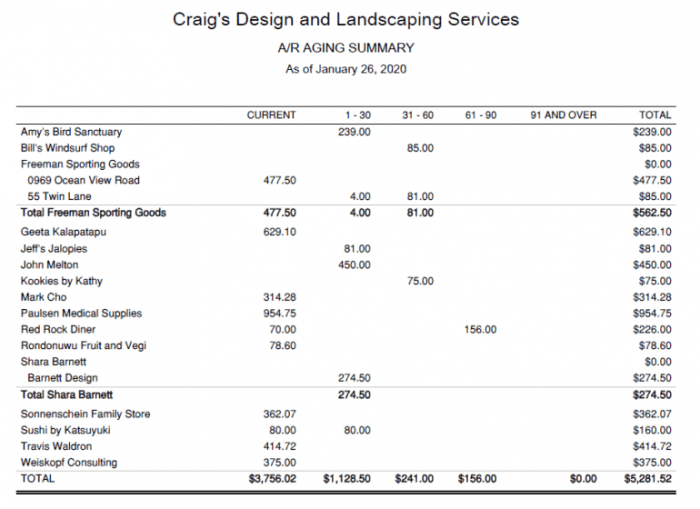
Accounts receivable aging refers to the classification of outstanding customer invoices based on their age or the time elapsed since they became due. It is a crucial aspect of financial management as it provides valuable insights into a company’s credit and collection practices and their impact on cash flow and profitability.
Aging accounts receivable can have significant consequences for a company. Overdue invoices can lead to delayed cash inflows, reduced liquidity, and increased bad debt expenses. Conversely, effective management of accounts receivable can improve cash flow, reduce credit risk, and enhance overall financial performance.
Causes of an Aging Accounts Receivable
Several factors can contribute to an aging accounts receivable, including:
- Slow-paying customers: Customers who consistently delay payments beyond the agreed-upon terms.
- Inefficient billing practices: Errors or delays in invoicing can result in late payments.
- Economic downturns: Economic slowdowns can lead to customers experiencing financial difficulties and delaying payments.
- Inadequate credit policies: Loose credit policies may result in accepting customers with poor credit histories.
- Lack of communication: Poor communication with customers regarding invoices and payment due dates can contribute to aging.
These factors can strain a company’s cash flow and increase the risk of bad debts.
Methods for Analyzing Accounts Receivable Aging
Companies use various techniques to analyze accounts receivable aging, including:
- Aging schedule: A report that classifies outstanding invoices into different age categories, such as current, 1-30 days past due, 31-60 days past due, and so on.
- Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): A metric that measures the average number of days it takes for a company to collect its accounts receivable. A higher DSO indicates slower collection practices.
- Credit risk analysis: Assessing the creditworthiness of customers to identify potential risks and develop appropriate credit policies.
These methods help companies identify problem areas and develop strategies to improve accounts receivable management.
Strategies for Managing Accounts Receivable Aging, An aging of a company’s accounts receivable indicates that
Effective management of accounts receivable involves implementing strategies such as:
- Establishing clear credit policies: Setting clear payment terms and conducting thorough credit checks on customers.
- Efficient invoicing and collection procedures: Automating invoicing, sending timely reminders, and implementing effective collection strategies.
- Customer relationship management: Building strong relationships with customers to foster timely payments.
- Offering incentives for early payment: Providing discounts or other incentives to encourage customers to pay invoices promptly.
- Outsourcing accounts receivable management: Partnering with specialized firms to handle collections and improve efficiency.
These strategies can significantly reduce accounts receivable aging and improve cash flow.
Impact of Accounts Receivable Aging on Financial Statements
Aging accounts receivable can impact a company’s financial statements in several ways:
- Balance sheet: Overdue accounts receivable can inflate the current assets section, leading to an overstatement of the company’s liquidity.
- Income statement: Uncollected accounts receivable can result in lower sales revenue and higher bad debt expenses, reducing net income.
- Financial ratios: Aging accounts receivable can negatively impact key financial ratios, such as the current ratio and gross profit margin.
Properly managing accounts receivable aging is crucial for maintaining accurate financial statements and ensuring a true reflection of a company’s financial performance.
Questions and Answers: An Aging Of A Company’s Accounts Receivable Indicates That
What is an aging accounts receivable?
An aging accounts receivable is a report that shows the age of a company’s unpaid invoices. It is used to track how long it takes customers to pay their bills and to identify any potential problems.
What are the causes of an aging accounts receivable?
There are a number of factors that can contribute to an aging accounts receivable, including slow-paying customers, inefficient billing practices, and economic downturns.
What are the consequences of an aging accounts receivable?
An aging accounts receivable can have a negative impact on a company’s cash flow and profitability. It can also be a sign of underlying financial problems.
What can businesses do to address an aging accounts receivable?
There are a number of steps that businesses can take to address an aging accounts receivable, including improving their collection practices, offering discounts for early payment, and working with customers to develop payment plans.