The decline of feudalism answer key embarks on a journey through history, illuminating the intricate factors that shaped the downfall of this once-dominant societal structure. From the rise of nation-states to the transformative power of technological advancements, this exploration delves into the complexities of feudalism’s demise.
Throughout this narrative, we will uncover the political, economic, social, intellectual, and regional forces that played a pivotal role in feudalism’s decline. By examining specific examples and tracing the evolution of ideas, this guide provides a comprehensive understanding of this pivotal historical period.
The Decline of Feudalism
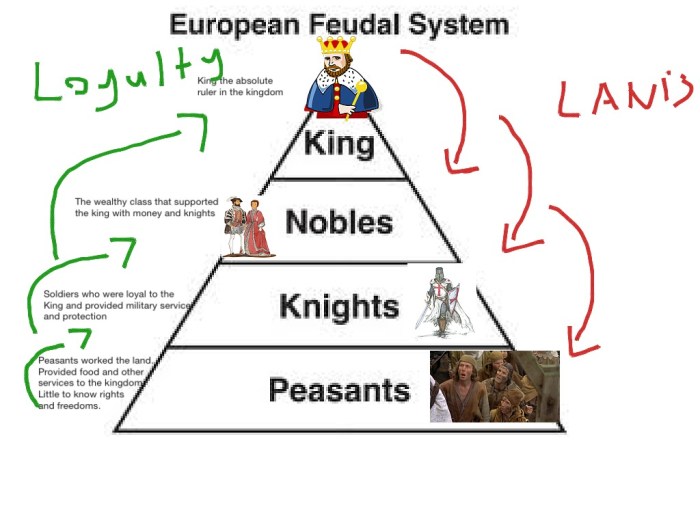
Feudalism, a dominant socio-economic and political system during the Middle Ages, gradually declined in Europe during the late Middle Ages and early modern period. This decline was driven by a complex interplay of political, economic, social, intellectual, and regional factors.
Political Factors
The weakening of feudal power structures was a major factor in the decline of feudalism. The rise of nation-states and centralized governments undermined the power of feudal lords and knights. The development of standing armies, funded by the growing wealth of monarchs, reduced the need for feudal levies and military support from vassals.
Warfare and military advancements also played a role. The introduction of gunpowder and new siege techniques made feudal fortifications less effective. The increasing cost of warfare and the need for larger, professional armies put a strain on feudal economies and led to the rise of mercenary forces.
Economic Factors
The shift from a feudal economy to a market economy was a significant factor in the decline of feudalism. The growth of trade and commerce undermined feudal economic practices, such as serfdom and the manorial system. Merchants and artisans gained wealth and influence, challenging the economic dominance of feudal lords.
Technological innovations and the rise of urban centers further contributed to feudal decline. The development of new agricultural techniques increased productivity, reducing the need for serf labor. The growth of cities provided alternative economic opportunities for peasants, weakening their ties to feudal lords.
Social Factors, The decline of feudalism answer key
Changing social structures and the emergence of new classes contributed to the decline of feudalism. The growth of literacy and education led to a more educated population, challenging traditional feudal values and hierarchies.
Religious movements, such as the Protestant Reformation, emphasized individualism and direct relationships with God, undermining the authority of the Catholic Church and the feudal order it supported.
Intellectual Factors
The rise of new ideas and philosophies challenged feudal values. The Renaissance and the Enlightenment promoted humanism, rationalism, and individualism, undermining the traditional feudal emphasis on hierarchy and tradition.
Scholars and philosophers argued for more equitable and just societies, questioning the legitimacy of feudal privilege and the divine right of kings.
Regional Variations
The decline of feudalism occurred at different paces and in different ways in different regions of Europe. In England, a strong centralized monarchy and the development of a common law system accelerated feudal decline. In France, feudalism persisted longer, due to the weakness of the monarchy and the power of the nobility.
External factors, such as the Crusades and the Mongol invasions, also influenced feudalism. The Crusades exposed Europeans to new ideas and technologies, while the Mongol invasions weakened feudal structures in Eastern Europe.
FAQ Guide: The Decline Of Feudalism Answer Key
What were the primary political factors that contributed to the decline of feudalism?
The weakening of feudal power structures, the rise of nation-states and centralized governments, and the impact of warfare and military advancements played significant roles in the decline of feudalism.
How did economic factors contribute to the decline of feudalism?
The shift from a feudal economy to a market economy, the growth of trade and commerce, technological innovations, and the rise of urban centers all undermined feudal economic practices.
What were the key social factors that influenced the decline of feudalism?
Changing social structures, the emergence of new classes, the growth of literacy and education, and the impact of religious movements and individualism contributed to the decline of feudal society.