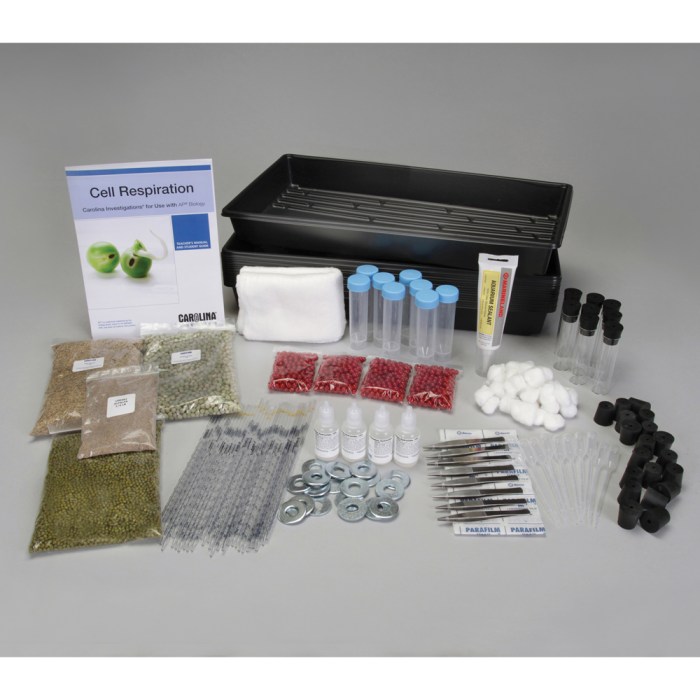
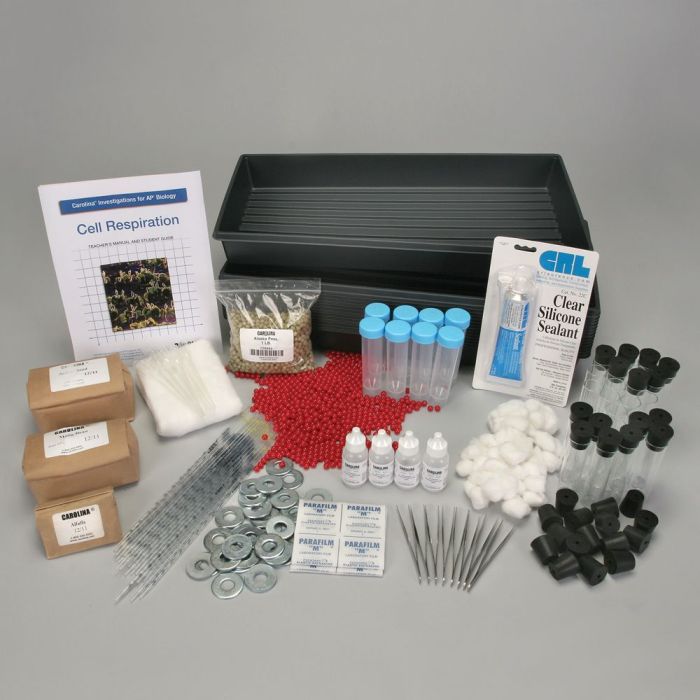
Carolina cell respiration for AP biology delves into the intricate mechanisms of cellular respiration, a fundamental process that underpins the survival and functioning of all living organisms. This journey begins with an exploration of the significance of cell respiration in biological systems, followed by a detailed examination of the three main stages involved: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Throughout this exploration, we will uncover the intricate regulation of cell respiration and its profound implications for cellular homeostasis and overall organismal function.
1. Carolina Cell Respiration Introduction

Cell respiration is a fundamental metabolic process that occurs in all living organisms. It involves the breakdown of organic molecules, such as glucose, to generate energy in the form of ATP. This energy is essential for various cellular activities, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis.
The overall process of cell respiration can be divided into three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Each stage occurs in a specific compartment of the cell and involves a series of enzymatic reactions.
2. Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cell respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm. It involves the breakdown of one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. This process also generates two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH, an electron carrier.
Glycolysis is regulated by several enzymes, including hexokinase and phosphofructokinase. These enzymes respond to changes in cellular energy levels and ensure that glycolysis is only active when ATP is needed.
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. It involves the oxidation of acetyl-CoA, a two-carbon molecule derived from pyruvate, to produce carbon dioxide and energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
The Krebs cycle is regulated by several enzymes, including citrate synthase and isocitrate dehydrogenase. These enzymes respond to changes in cellular energy levels and ensure that the Krebs cycle is only active when ATP is needed.
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cell respiration and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, which results in the production of water and ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation is carried out by a series of protein complexes known as the electron transport chain. These complexes pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase.
5. Regulation of Cell Respiration
Cell respiration is regulated by several factors, including oxygen availability, pH, and ATP levels. When oxygen is available, cells primarily use oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP. However, when oxygen is limited, cells switch to anaerobic respiration, which produces ATP without using oxygen.
pH also affects cell respiration. The enzymes involved in cell respiration are most active at a neutral pH. Changes in pH can inhibit enzymatic activity and slow down the rate of cell respiration.
6. Applications of Cell Respiration, Carolina cell respiration for ap biology
Cell respiration is essential for various biological processes. It provides the energy needed for muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and the synthesis of proteins and other molecules.
Cell respiration also plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. By producing ATP, cell respiration helps to regulate cellular processes, such as ion transport, protein synthesis, and gene expression.
Question Bank: Carolina Cell Respiration For Ap Biology
What is the significance of cell respiration?
Cell respiration is essential for generating energy in the form of ATP, which powers various cellular processes and maintains cellular homeostasis.
What are the three main stages of cell respiration?
The three main stages of cell respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
How is cell respiration regulated?
Cell respiration is regulated by various factors, including oxygen availability, pH, and ATP levels.